DeFi 101: What is staking?
What's PoW and PoS? What is staking?

Before I explain what staking is, it's important to understand what proof of work (PoW) and proof of stake (PoS) are.
Proof of Work (PoW):
Proof of Work (PoW) is a decentralized consensus mechanism that uses computational effort to validate transactions and secure blockchain networks, removing the need for a central authority. Miners compete to solve complex cryptographic puzzles to create new blocks and are rewarded with cryptocurrency for their work. While this method provides security and decentralization, it is energy-intensive and can lead to slow transaction speeds and potential centralization among large mining entities.
In other words, to mine coins, you will need to invest resources, mostly hardware and electricity. Usually, you'll need hardware that is built specifically for mining purposes. They tend to lose value in a few years, as new hardware is more powerful and/or energy efficient.
While this can be interesting in countries with very low electricity costs, the returns tend to be quite limited due to the size of the initial investment.
Proof of Stake (PoS):
Proof of Stake (PoS) is a blockchain consensus mechanism where participants, called validators, stake (or lock up) their own cryptocurrency as collateral to validate transactions and create new blocks. Validators are then randomly chosen to create new blocks, with the chance of selection proportional to their staked amount. PoS offers significant energy efficiency and security advantages over (PoW) by eliminating the energy-intensive computational mining process.
In other words, you need to own/buy the asset that you want to stake, in order to generate staking rewards.
Staking explained:
Staking in crypto is like putting money in a savings account, but instead of earning interest from a bank, you earn rewards from helping run a blockchain.
Here’s the breakdown:
- What it is:
You "lock up" some of your cryptocurrency (like Ethereum or Solana) so the network can use it to keep things secure and process transactions. - Why it exists:
Blockchains that use proof of stake don’t rely on energy-hungry mining. Instead, they need people to commit (stake) their coins as a kind of trust signal that they’ll play by the rules. - What you get:
In return for staking, you earn rewards (usually the same currency you staked), similar to earning interest. - Risks:
- Your coins are often locked up, so you can’t always access them immediately.
- The value of the coin could drop, which can offset the rewards.
- If you stake through a shady platform, you might lose funds.
Staking by yourself is quite complex. You will need to set-up and run a validator node. For Ethereum, a node requires 32 ETH. At current prices, that's well over $100k, and few people hold that much Ethereum. Also, coins are locked-up and don't offer much flexibility. These issues are the reason why liquid staking became so popular.
The term staking is often used to describe both and can be confusing, but make sure you understand which type of staking someone is talking about.
As you can see below, staking is the biggest category in crytpo, according to Defillama.
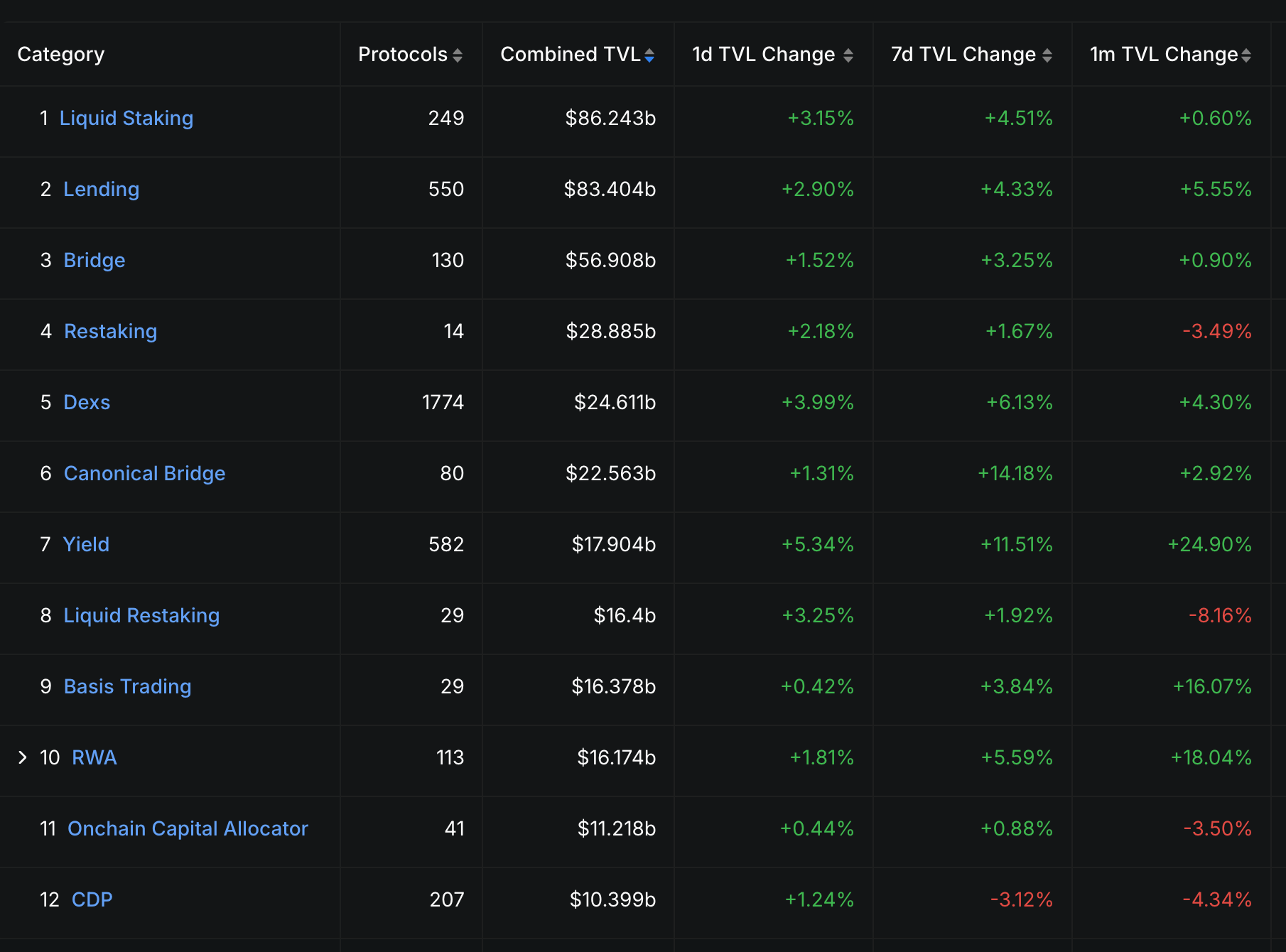
What is liquid staking?
Did you notice something in the picture above? There's "liquid staking", "restaking", and "liquid restaking". What is all this?
Liquid staking is essentially the next step after "normal" staking.
Normally, when you stake crypto, your coins are locked up. You can’t use or move them until the staking period ends. That’s the trade-off for earning rewards.
Liquid staking solves this by giving you a special “receipt token” when you stake.
Here’s how it works:
- You stake your crypto (say 1 ETH).
- Instead of losing access to it, you get a liquid staking token (like stETH from Lido, or rETH from Rocket Pool).
- This token represents your staked ETH plus the rewards it earns.
- You can use this token in other ways: trade it, lend it, provide liquidity; while your original ETH stays locked and keeps earning rewards.
🔑 Why people like it:
- You still earn staking rewards.
- You don’t lose flexibility: you can move, sell, or use the “receipt token” right away.
⚠️ Risks to know:
- Smart contract risk (bugs in the staking platform).
- Price differences (the liquid staking token might not always equal the full value of the underlying crypto).
- Centralization (if too many people use the same liquid staking provider).
The biggest liquid staking protocol is Lido (stETH & wstETH).
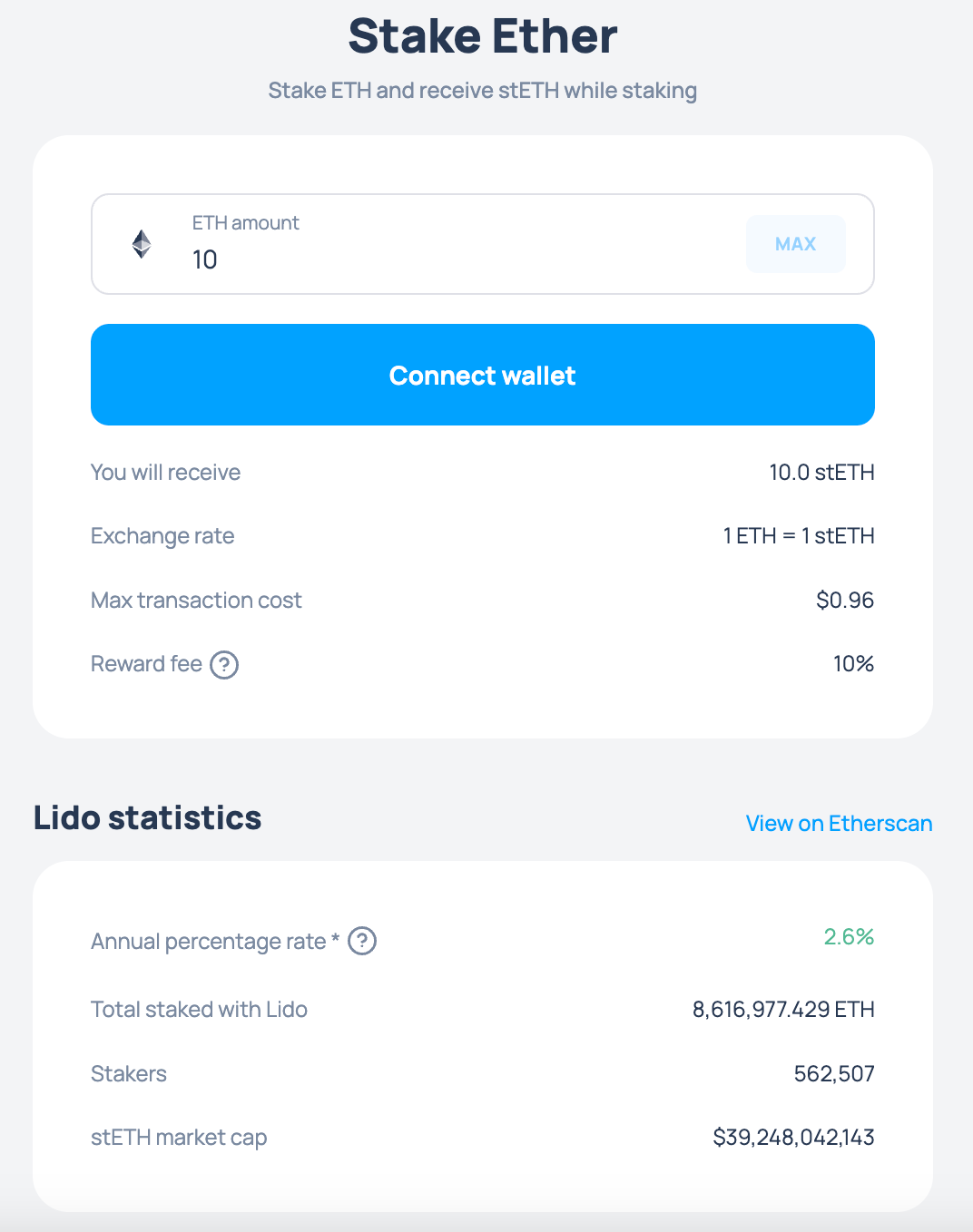
If you stake 1 ETH, you will receive 1 stETH (staked ETH). If you hold stETH, you will receive additional stETH, coming from the staking rewards.
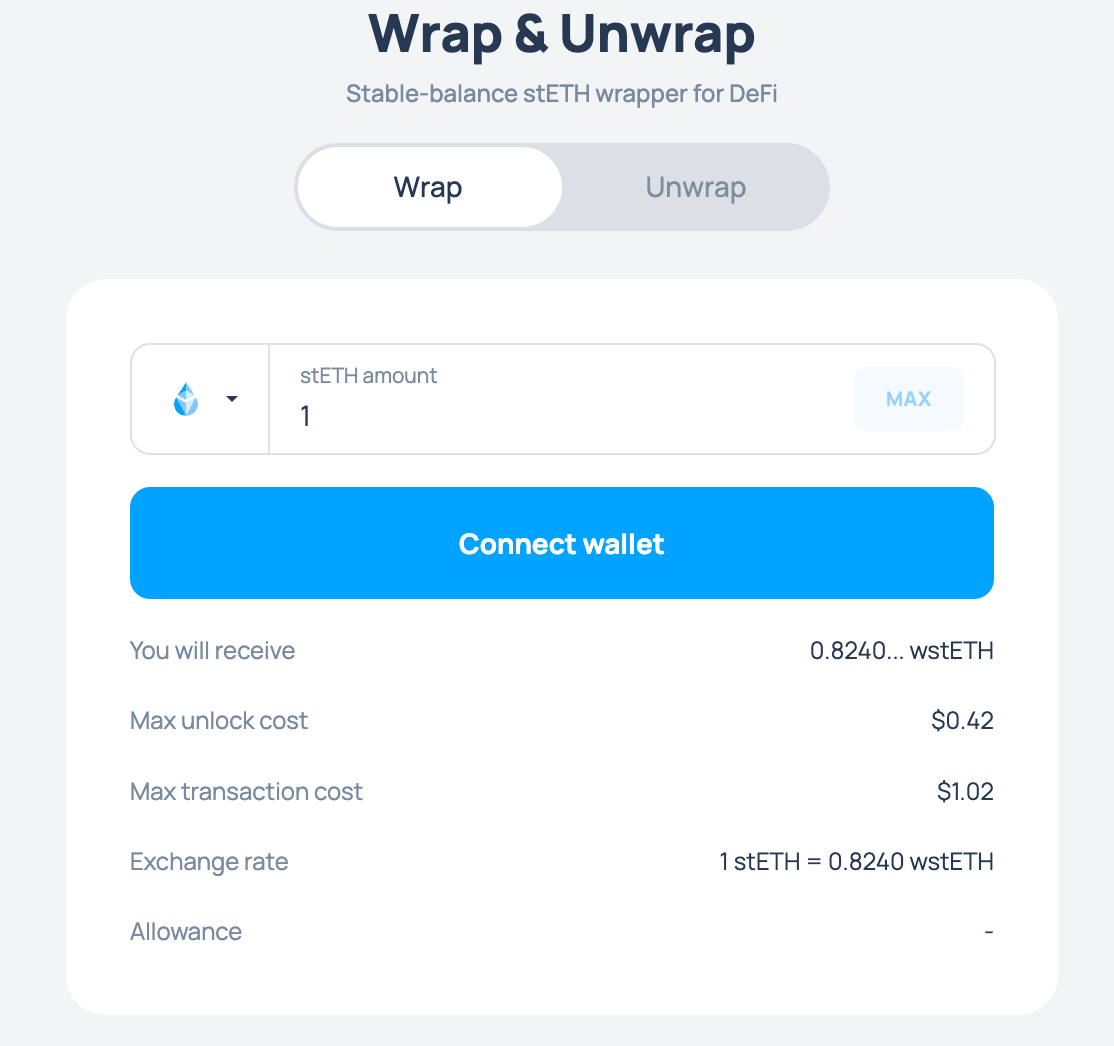
You can convert your stETH into wstETH (wrapped staked ETH). wstETH basically is a "compounding" version. Meaning that if you bought 1 wstETH with 1.1 ETH (or stETH), in one year, this 1 wstETH should give you around 1.126 ETH.
What is restaking?
Restaking means using the same staked crypto to secure more than one network or service at the same time.
Normally, when you stake (say ETH), it only helps secure the Ethereum blockchain.
With restaking, your staked ETH can also help secure other protocols (like data services, bridges, or oracles) — and you earn extra rewards for doing so.
🔹 How it Works (simplified):
- You stake your ETH (either directly as a validator or via liquid staking like stETH).
- Instead of just leaving it there, you “restake” it into a system like EigenLayer.
- EigenLayer then lets new services borrow Ethereum’s security by using your restaked ETH as collateral.
- You get paid more rewards for providing that extra security.
🔹 Why it’s Useful:
- New projects don’t need to build their own army of validators. They can piggyback on Ethereum’s security.
- Stakers earn more yield without adding more ETH.
- It makes Ethereum’s ecosystem stronger and more secure (in theory).
🔹 Risks of Restaking:
- Slashing risk: if one of the services you help secure misbehaves, your staked ETH could be penalized.
- Complexity risk: more moving parts = higher chance of bugs or failures.
- Centralization: if restaking platforms become too dominant, it could concentrate power.
👉 Analogy:
Imagine you already deposited money in a bank to earn interest.
Restaking is like letting a trusted company use that same deposit as insurance for multiple projects. You get extra returns, but if something goes wrong, you could lose part of your money.
The biggest restaking protocol is Eigenlayer. After Eigenlayer's launch, many liquid restaking protocols launched.
What is liquid restaking?
Liquid restaking = restaking with a liquid token.
Instead of locking your ETH directly into EigenLayer (or another restaking platform), you deposit it through a liquid restaking protocol. In return, you get a new token (like eETH, ezETH, or rsETH) that represents your restaked position.
- Your ETH is staked + restaked in the background.
- You earn both staking rewards + restaking rewards.
- You also get a liquid token you can trade, lend, or use in DeFi: just like with liquid staking.
🔹 Benefits
- Liquidity: You aren’t locked up; you can still use the liquid restaking token.
- Extra rewards: Earn more than plain staking.
- Composability: The token can plug into DeFi (lending, LP, collateral).
🔹 Risks
- Stacked risk layers: combines staking risk + liquid staking risk + restaking risk.
- Smart contract vulnerabilities (multiple protocols involved).
- Slashing exposure across all the networks your ETH is securing.
- Depeg risk: the liquid restaking token might trade below its “true” value.
👉 Analogy:
It’s like putting your money in a savings account (staking), letting it insure multiple businesses at once (restaking), and getting a tradeable certificate you can use in other investments (liquid token).
Conclusion
Hopefully you're not feeling more lost than when you started reading this thread.
If you want to stake ETH, use Lido or a liquid restaking protocol. The biggest one, by far, is Etherfi. In early/mid 2024 there was a massive restaking craze due to Eigenlayer's airdrop. It has since cooled down a lot.
Check the next part in this guide: What is a money market?





Comments ()